Associating the BART Server with a Database Server v9
After configuring the BART server, you need to associate it with the database server whose backup you want to manage with BART. You can do one of the following:
- Use the PEM console to modify the properties of an existing monitored database server to map it to the newly configured BART server.
- Use the PEM console to create a new monitored database server, and map it to the newly configured BART server.
To map the BART server to a new PEM database server, right-click the PEM Server Directory node and select Create > Server. Enter the details on all the generic tabs and then enter the BART-specific details on the BART tab.
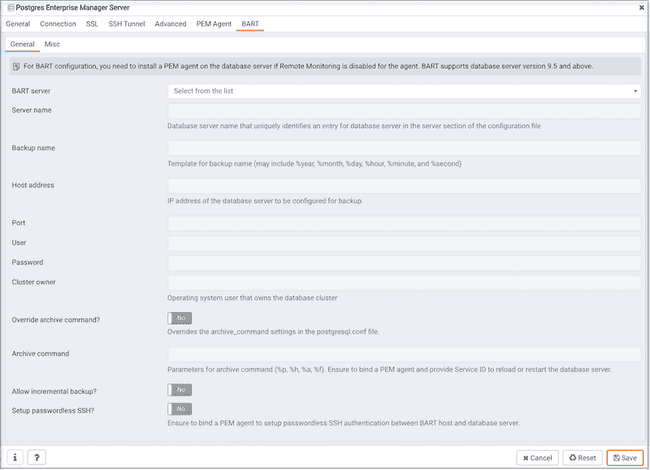
Use the fields on the General tab to describe the general properties of the BART Server that will map to the PEM server:
- Use the
BART serverfield to select the BART server name. All the BART servers configured in the PEM console will be listed in this drop down list. - Use the
Server namefield to specify a name for the database server that you want to backup using the BART server. This name gets stored in the BART configuration file. - Use the
Descriptionfield to specify the description of the database server. - Use the
Backup namefield to specify a template for user-defined names to be assigned to the backups of the database server. If you do not specify a backup name template, then the backup can only be referenced in BART sub-commands by the BART assigned, integer backup identifier. - Use the
Host addressfield to specify the IP address of the database server that you want to configure for backup. - Use the
Portfield to specify the port to be used for the database that you want to backup. - Use the
Userfield to specify the user of the database that you want to backup using BART through PEM console. If you want to enable incremental backups for this database server, then the user must be a superuser. - Use the
Passwordfield to specify the password for the user of the database that you want to backup. - Use the
Cluster ownerfield to specify the Linux operating system user account that owns the database cluster. This is typicallyenterprisedbfor Advanced Server database clusters installed in the Oracle databases compatible mode, orpostgresfor PostgreSQL database clusters and for Advanced Server database clusters installed in the PostgreSQL databases compatible mode. - Use the
Override archive command?switch to specify if you want to override the archive command in the database server'spostgresql.conffile. If you override the archive command, the database server will be restarted or database configurations will be reloaded after the server gets added. - Use the
Archive commandfield to specify the desired format of the archive command string. Ensure to bind a PEM agent and provideService IDto reload the database configuration or restart the server. - Use the
Archive pathfield to store the archived WAL files. The default location is the BART backup catalog. This parameter is added from BART version 2.5.2 onwards. - Use the
Allow incremental backup?switch to specify if incremental backup should be enabled for this database server. - Use the
Setup passwordless SSH?switch to specify if you want to create SSH certificates to allow passwordless logins between the database server and the BART server. You must ensure that a PEM agent is bound to the server before configuring passwordless SSH authentication. Passwordless SSH will not work for a database server that is being remotely monitored by a PEM agent.
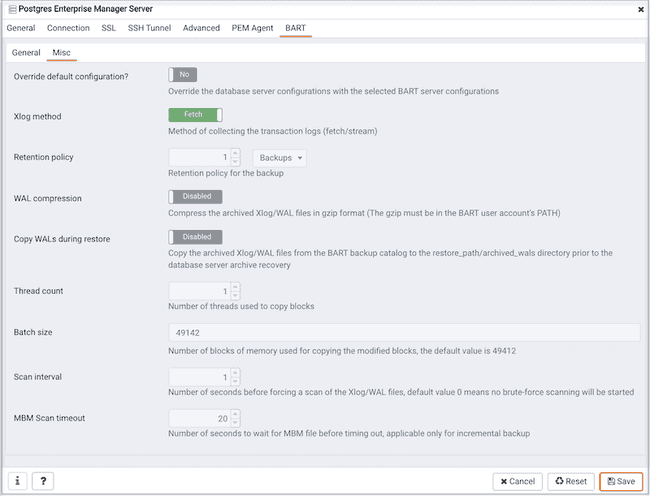
Use the fields on the Misc tab to describe the miscellaneous properties of the BART Server:
- Use the
Override default configuration?Switch to specify if you want to override the BART server configurations with the specific database server configurations. - Use the
Xlogmethod to specify how the transaction log should be collected during the execution ofpg_basebackup. - Use the
Retention policyfield to specify the retention policy for the backup. This determines when an active backup should be marked as obsolete, and hence, be a candidate for deletion. You can specify the retention policy in terms of number of backup or in terms of duration (days, weeks, or months). - Use the
WAL compressionswitch to specify if you want to compress the archived Xlog/WAL files in Gzip format. To enable WAL compression, the gzip compression program must be present in the BART user account’s PATH. The wal_compression setting must not be enabled for those database servers where you need to take incremental backups. - Use the
Copy WALs during restorefield to specify how the archived WAL files are collected when invoking the RESTORE operation. Set to enabled to copy the archived WAL files from the BART backup catalog to the \<restore_path>/archived_wals directory prior to the database server archive recovery. Set to disabled to retrieve the archived WAL files directly from the BART backup catalog during the database server archive recovery. - Use the
Thread countfield to specify the number of threads to copy the blocks. You must setthread countto1if you want to take a backup with thepg_basebackuputility. - Use the
Batch sizefield to specify the number of blocks of memory used for copying modified blocks, applicable only for incremental backups. - Use the
Scan intervalfield to specify the number of seconds after which the WAL scanner should scan the new WAL files. - Use the
MBM scan timeoutfield to specify the number of seconds to wait for MBM files before timing out, applicable only for incremental backups. - Use the
Workersfield to specify the number of parallel worker processes required to stream the modified blocks of an incremental backups to the restore host.