Audit Manager v9
You can use the PEM Audit manager to configure, enable, and disable audit logging of EDB Postgres Advanced Server instances. The Audit manager also enables audit log collection, allowing you to view log data on the Audit Log Dashboard.
To run the Audit manager wizard, select Audit manager... from the PEM client Management menu. Audit manager opens, displaying the Welcome dialog:
Click Next to continue:
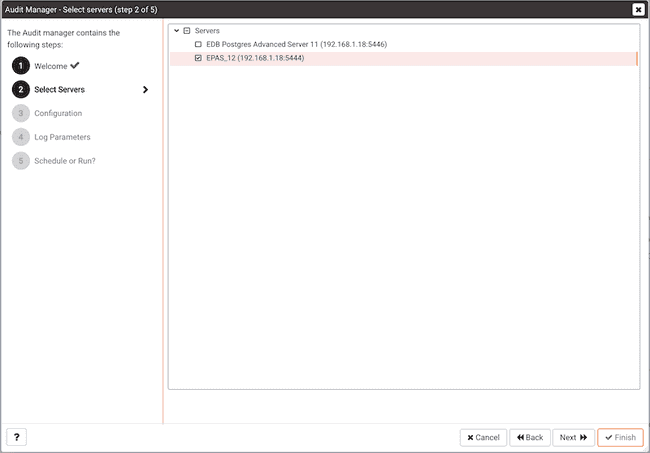
Use the Select servers tree control to specify the servers to which the auditing configuration will be applied. To make a server available in the tree control, you must provide the Service ID on the PEM Server dialog. Note that only EDB Postgres Advanced Server supports auditing; PostgreSQL servers will not be included in the tree control.
Click Next to continue:
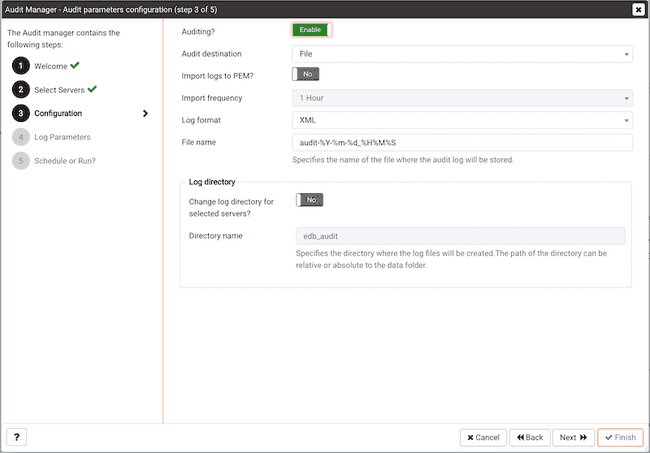
Use the controls on the Audit parameters configuration dialog to specify configuration details that will be applied to each server:
- Use the
Auditingswitch toEnableorDisableauditing on the specified servers. - Use the
Audit destinationdrop-down to select a destination for the audit logs; selectFileorSyslog. Please note this feature is supported on Advanced Server 10 and newer releases only. - Use the
Import logs to PEMswitch to instruct PEM to periodically import log records from each server to the PEM Server. Set the switch toYesto import log files; the default isNo. - Use the
Import frequencydrop-down listbox to specify how often PEM will collect log records from monitored servers when log collection is enabled. - Use the
Log formatdrop-down listbox to select the raw log format that will be written on each server. If log collection is enabled, the PEM server will use CSV format. - Use the
File namefield to specify the format used when generating log file names. By default, the format is set toaudit-%Y-%m-%d_%H%M%Sif log collection is enabled.
Use fields in the Log directory box to specify information about the directory in which the log files will be saved:
- Move the
Change log directory for selected servers?switch toYesto enable theDirectory namefield. - Use the
Directory namefield to specify the name of the directory on each server into which audit logs will be written. The directory specified will be created as a sub-directory of thedatadirectory on the server.
Click Next to continue:
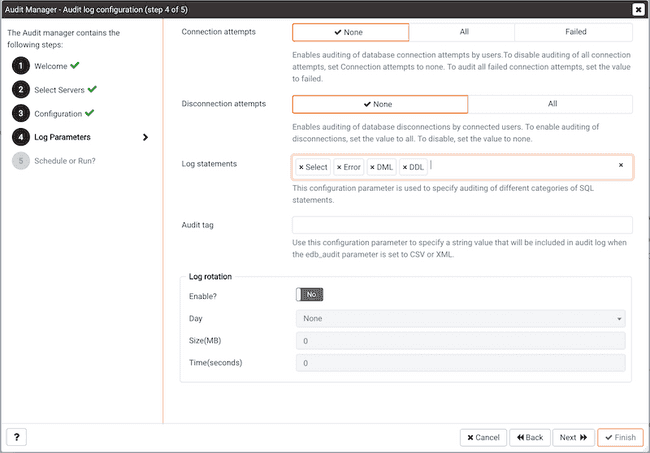
The Audit log configuration dialog is only available if you have specified a value of Enable in the Auditing field. Use the controls on the Audit log configuration dialog to specify log configuration details that will be applied to each server:
Use the
Connection attemptsswitch to specify if connection attempts should be logged. Specify:Noneto disable connection logging,Allto indicate that all connection attempts will be logged, orFailedto log any connection attempts that fail.Use the
Disconnection attemptsswitch to specify if disconnections should be logged. SpecifyNoneto specify that disconnections should not be logged, orAllto enable disconnection logging.Use the
Log statementsfield to specify the statement types that will be logged. Click within the field, and select from:- Select - All statements that include the SELECT keyword will be logged
- Error - All statements that result in an error will be logged.
- DML - All DML (Data Modification Language) SQL statements will be logged.
- DDL - All DDL (Data Definition Language) SQL statements (those that add, delete or alter data) will be logged.
- Check the box next to
Select Allto select all statement types. - Check the box next to
Unselect Allto deselect all statement types.
Use the
Audit tagfield to specify a tracking tag for the collected logs. Please note that audit tagging functionality is available only for Advanced Server versions 9.5 and later. If you are defining auditing functionality for multiple servers, and one or more of the servers are version 9.5 or later, this field will be enabled, but if selected, tagging functionality will only apply to those servers that are version 9.5 or later.
Use the fields in the Log rotation box to specify how the log files are managed on each server:
- Use the
Enable?switch to specify that logfiles should be rotated. Please note that a new log file should be used periodically to prevent a single file becoming unmanageably large. - Use the
Daydrop-down listbox to select a day or days on which the log file will be rotated. - Use the
Size (MB)field to specify a size in megabytes at which the log file will be rotated. - Use the
Time (seconds)field to specify the number of seconds between log file rotations.
Click Next to continue:
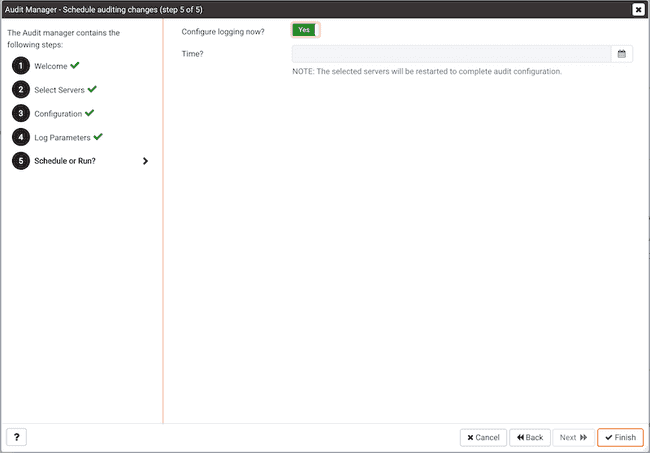
Use the Schedule auditing changes dialog to specify when the new configuration will be applied to the servers:
- Set the
Configure logging now?switch toYesto apply the configuration immediately. - Use the
Time?selector to schedule the audit configuration for a later time; use the date and time selectors to specify the date and time at which the PEM server will apply the configuration.
Click the Finish button to schedule a job to apply the configuration to each server. The job will consist of two tasks. One task will update the audit logging configuration on the server, and one task will reload the server with the new configuration.
The scheduled jobs can be viewed in the Task Viewer, and the results in the Log Viewer when opened from the appropriate server or agent.