Configuring a BART Server v9
You can use the Create–BART server dialog to register an existing BART server with the PEM server. To access the dialog, right-click on the BART Servers node and select Create-BART Server.
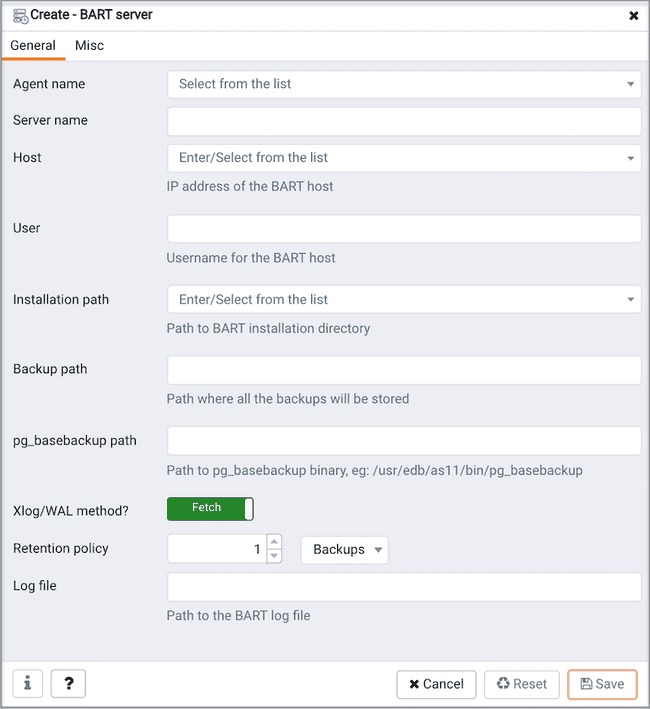
Use the fields on the General tab to describe the general properties of the BART Server:
Use the
Agent Namefield to select the agent that you want to configure as a BART server. Only those PEM agents that are supported for BART are listed in the drop-down list.Use the
Server Namefield to specify a user-friendly name for the server. The name specified will identify the server in the Browser tree.Use the
Hostfield to specify the IP address of the host or agent where BART is installed.Use the
Userfield to specify the user name that will be used for performing all the BART operations. You can either use theenterprisedb(for Advanced Server) orpostgres(for PostgreSQL) database user account or you can create a new BART user account. This user must be an operating system user who owns the BART backup catalog directory.Use the
Installation pathfield to specify the directory path where BART is installed on the host or BART server.Use the
Backup pathfield to specify the file system parent directory where all BART backups and archived WAL files will be stored.Use the
pg_basebackup_pathfield to specify the path to thepg_basebackuputility.Use the
Xlog/WALmethod field to specify how the transaction log should be collected during the execution of pg_basebackup. The default option isfetch; it specifies that the transaction log files will be collected after the backup has completed. Set theXlogmethod tostreamto stream the transaction log in parallel with the full base backup creation. If streaming is used, themax_wal_sendersconfiguration parameter in thepostgresql.conffile for affected database servers must account for an additional session for the streaming of the transaction log (the setting must be a minimum of 2).For more information about Xlog method, see:
https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/app-pgbasebackup.html
Use the
Retention policyfield to specify the retention policy for the backup. This determines when an active backup should be marked as obsolete, and hence, be a candidate for deletion. You can specify the retention policy in terms of number of backup or in terms of duration (days, weeks, or months).Use the
Log filefield to specify the path to BART log file. This is an optional field.
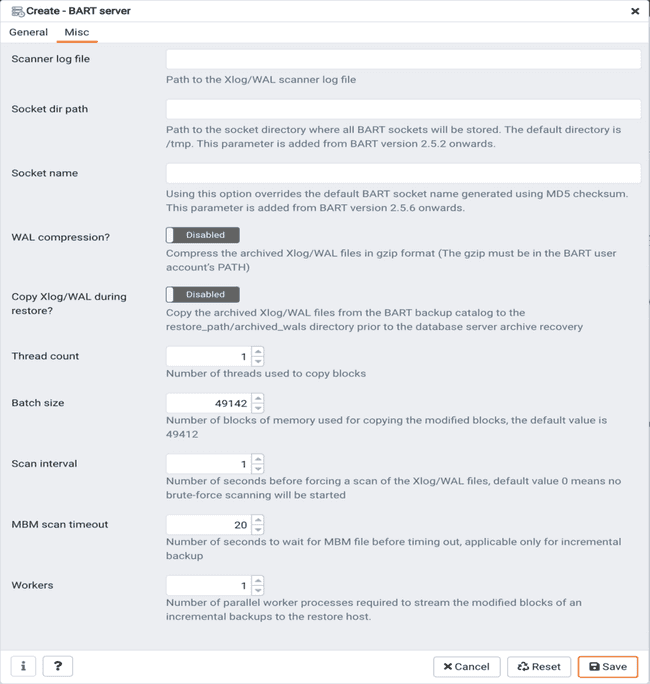
Use the fields on the Misc tab to describe the backup-related properties of the BART Server:
- Use the
Scanner log filefield to specify the path to the Xlog/WAL scanner log file. This is an optional field; BART does not create a WAL scanner log file if you do not specify the path. - Use the
Socket dir pathfield to specify the path to the socket directory where all BART sockets will be stored. The default directory is/tmp. This parameter is added from BART version 2.5.2 onwards. - Use the
Socket namefield to specify a user-friendly BART socket file name. Using this option overrides the default BART socket name generated using MD5 checksum. This parameter is added from BART version 2.5.6 onwards. - Use the
WAL compression?switch to specify if you want to compress the archived Xlog/WAL files in Gzip format. To enable WAL compression, the gzip compression program must be present in the BART user account’s PATH. The WAL compression setting must not be enabled for those database servers where you need to take incremental backups. - Use the
Copy WALs during restore?field to specify how the archived WAL files are collected when invoking the RESTORE operation. Set to enabled to copy the archived WAL files from the BART backup catalog to therestore_path/archived_walsdirectory prior to the database server archive recovery. Set todisabledto retrieve the archived WAL files directly from the BART backup catalog during the database server archive recovery. Enabling this option helps you save time during the restore operation. - Use the
Thread countfield to specify the number of worker threads for copying blocks or data files from the database server to the BART backup catalog. Specify athread countof1if you want to take the backup using thepg_basebackuputility. - Use the
Batch sizefield to specify the number of blocks of memory used for copying modified blocks. This is applicable only for incremental backups. - Use the
scan intervalfield to specify the number of seconds after which the WAL scanner should scan the new WAL files. - Use the
MBM scan timeoutfield to specify the number of seconds to wait for MBM files before timing out. This is applicable only for incremental backups. - Use the
Workersfield to specify the number of parallel worker processes required to stream the modified blocks of an incremental backups to the restore host.